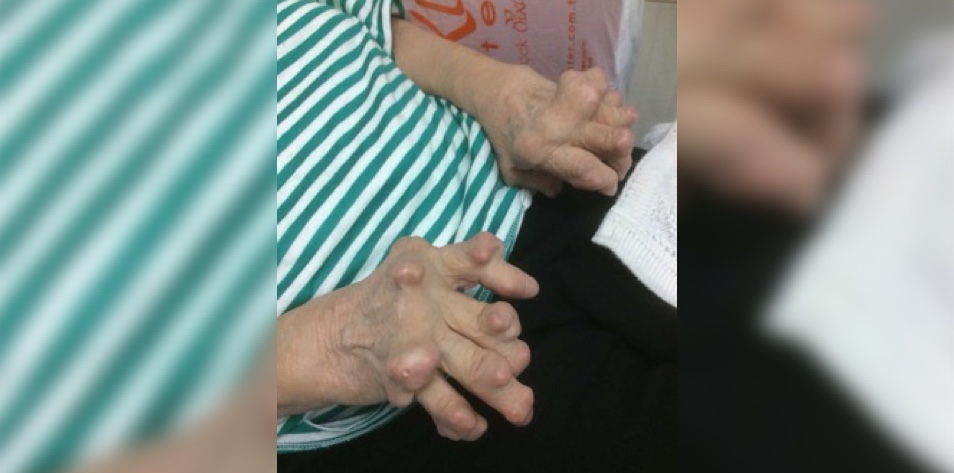
A 60-year-old presents to the dermatologist with the sudden onset of multiple painful growths on the upper extremities that began within three months of starting methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis.
On examination, the patient has numerous subcutaneous nodules on the bilateral hand digits. This clinical entity is known as accelerated rheumatoid nodulosis. Unlike typical rheumatoid nodules that are usually isolated and non-tender overlying bony protuberances, accelerated rheumatoid nodulosis is characterized by the rapid growth of multiple, often symmetrically distributed and painful nodules.
Accelerated rheumatoid nodulosis is usually triggered by disease-modifying anti-rheumatic medication, most commonly with methotrexate. Nodules typically regress with cessation of methotrexate and re-appear with restarting methotrexate.
Further Reading
- Rheumatoid Nodules
- Rheumatoid arthritis: A review of the cutaneous manifestations
- Accelerated cutaneous nodulosis during methotrexate therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis
References
- Williams FM, Cohen PR, Arnett FC. Accelerated cutaneous nodulosis during methotrexate therapy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998 Aug;39(2 Pt 2):359-62. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70390-1. PMID: 9703153.
- Sayah A, English JC 3rd. Rheumatoid arthritis: a review of the cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005 Aug;53(2):191-209; quiz 210-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2004.07.023. PMID: 16021111.
Want more clinical cases?
Join Figure 1 for free and start securely collaborating with other verified healthcare professionals on more than 100,000 real-world medical cases just like this one.