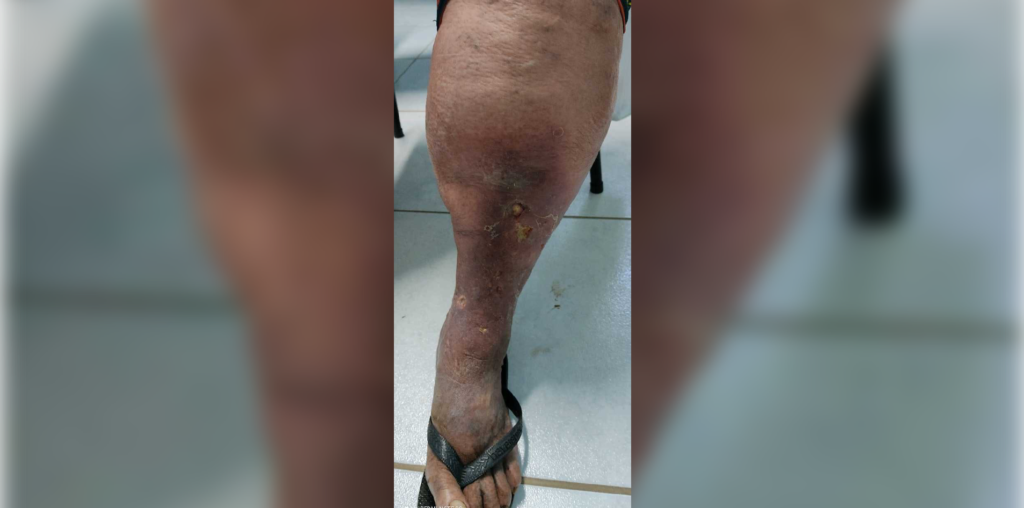
A 68-year-old with a history of chronic tobacco use presents with several years of progressively worsening swelling and discoloration on the bilateral lower extremities. They have noticed recent increased heaviness when walking, and a feeling of tightening along the medial aspects of both legs. On examination, the patient is morbidly obese, and firm red-brown plaques with fibrotic, constricted, band-like appearances are noted along the pretibial shins. Doppler ultrasound demonstrates superficial venous reflux in the lower limbs.
This distinctive fibrotic narrowing with red-brown discoloration on the distal lower extremities is often referred to as an “inverted champagne bottle” appearance in a clinical entity known as lipodermatosclerosis. It is strongly associated with longstanding venous insufficiency and can be complicated by the development of chronic, non-healing venous ulcers. Diagnosis may be supported by characteristic histologic findings of sclerosing panniculitis and ultrasound findings of dermal thickening and tissue calcification in the affected skin.
First-line treatment for lipodermatosclerosis involves compression stockings, leg elevation, and risk factor modification such as weight loss, smoking cessation, and increased physical activity. Adjunctive pharmacologic treatment includes stanozolol, danazol, pentoxifylline, and intralesional steroids.
Further Reading
References
- Kirsner RS, Pardes JB, Eaglstein WH, Falanga V. The clinical spectrum of lipodermatosclerosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993 Apr;28(4):623-7. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70085-8. PMID: 8463465.
- Miteva, M., Romanelli, P. and Kirsner, R.S. (2010), Lipodermatosclerosis. Dermatologic Therapy, 23: 375-388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8019.2010.01338.
- Woźniak W, Danowska A, Mlosek RK. The use of high-frequency skin ultrasound in the diagnosis of lipodermatosclerosis. J Ultrason. 2021;20(83):e284-e290. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2020.0050. Epub 2020 Dec 18. PMID: 33500796; PMCID: PMC7830071.
Want more clinical cases?
Join Figure 1 for free and start securely collaborating with other verified healthcare professionals on more than 100,000 real-world medical cases just like this one.